Stéphanie Bouillot, CEA Research Technician
Sophie Gerbaud, CEA Engineer
The main aim of the R&D activity of the platform is to develop quantitative and qualitative imaging tools based on High Content Screening technology (HCS) for the discovery of new bioactive compounds by robotic screening or for their validation and characterization by an in-depth cellular profiling.
Left : IncuCyte ZOOM (Sartorius) for long-term live imaging of cells with or without fluorescent staining (phase contrast, A488/GFP, Cy3), from few hours to several days thanks to a temperature, CO2 and humidity regulated environment.
Right: CellInsight CX7 confocal LED microscope (Thermo Scientific) for automated image acquisition and analysis of live or fixed cells, in brightfield, widefield or confocal mode (7 wavelengths available), at different magnifications (4x to 60x).
High Content Screening is a fluorescent automated imaging technology allowing the screening of compounds on fixed or live cells. It allows the rapid imaging of many cells on a given experimental condition and the automatic extraction of huge sets of quantitative and qualitative features at the cell level (count, area, intensity, form… for a number of objects like cells, nuclei, intracellular compartments, fibers…).
Using this technology, we develop a cellular profiling strategy in order to speed up the validation and characterization step of the bioactive compounds (Hits) selected by
robotic screening on our platform. For that purpose, different cell-based assays were set up in 96-well plates and allow the study of compounds effect on various essential constituents and processes of the cell (
Figure 1). For each experimental test, specific automated image acquisition and analysis protocols are developed with a view to routine applications. Huge data sets are produced and require the development and integration of computerized methods for object segmentation, extraction of specific descriptors, pattern recognition and statistical modelling.
 Figure 1: Cellular profiling strategy using HCS/HCA
Figure 1: Cellular profiling strategy using HCS/HCA
Furthermore, in the context of
Gen&Chem scientific projects, we apply this cell profiling strategy to the study and the understanding of the regulation mechanisms of innate immunity and inflammation. More especially our goal is to discover new interesting chemical probes targeting DeUBiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) which represent major actors of these cellular functions. Cell-based assays have been developed to quantify with accuracy either the TNFα-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB or autophagy (
Figure 2). These assays were used for the screening of a set of known chemical compounds in dose-response and for the study of the genetic extinction (shRNA) of few DUBs (ongoing projects).
 Figure 2: Cell-based assay for autophagy quantification.
Figure 2: Cell-based assay for autophagy quantification.
HeLa cells expressing LC3, a specific autophagosome marker, coupled to GFP were stained with Hoechst for nuclei recognition. Images of Hoechst and GFP channels were acquired with INCell Analyzer 1000 (20x obj). Then using INCell Investigator software, images were processed leading to the extraction of quantitative and qualitative features as the number of cells, the intensity of each staining, the shape or the area of nuclei, cells and autophagosomes.
Since 2011, HCS activity is open to collaborators from IRIG. The access conditions as well as the available equipment are detailed and explained in a
charter addressed to the users.
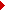 Skills and collaborations: Few examples.
Skills and collaborations: Few examples.
• Cell-based assays for HCS/HCA applications.